![]()
Big data analytics is playing an instrumental role in improving supply chain management. It resolves several pain points at strategic, operational, and tactical levels. Big data is making an impact on all supply chain activities. It ranges from improving delivery times to identifying ways to reduce the communication gap between manufacturers and suppliers. Analytics reports enable decision-makers to achieve operational efficiency and monitor performance to improve productivity. Supply chain analytics augment data-driven decisions to reduce costs and improve service levels. This blog explores the benefits of using big data in supply chains.
Consumer behavior and usage patterns:
Leading telecom businesses are actively investing in big data analytics to analyze the usage patterns and habits of their customers. The information gathered from the analytics report enables businesses to retain their subscribers and increase revenue significantly.
For instance, Vodafone is also using big data analytics to predict network growth and plan network expansions efficiently.
Enhanced inventory management:
Big box retailers and top online stores with a sizeable inventory have to overcome several challenges. Big data analytics enables operation managers to get a minute-by-minute overview of operations and identify bottlenecks that slow down supply chain processes. Additionally, consumer trends also enable businesses to promote best selling products and optimize inventory.
For instance, Amazon uses big data analytics in its inventory management. It selects warehouses based on the proximity of its vendors and customers to reduce distribution costs. Amazon uses big data analytics to distribute inventory according to customer preferences in a particular area.
Streamlined E-commerce:
Online retailers like Snapdeal and Flipkart use big data analytics to streamline their management processes. For instance, Flipkart relies on big data to ensure top-notch supply chain management. Flipkart improves its algorithms to accurately predict delivery dates, increase warehouse automation, and optimize routes through advanced mobile technology.
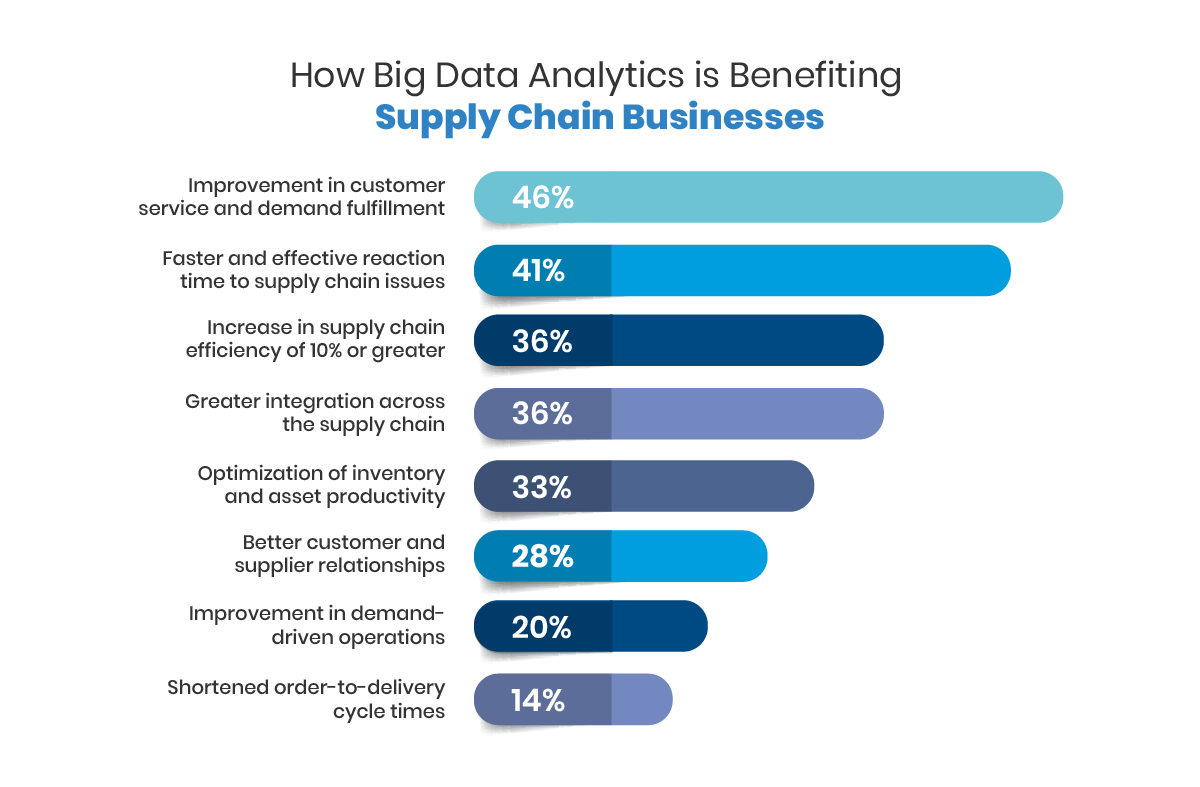
How does this impact the supply chain process?
Improved traceability:
Product traceability is key to successful supply chain operations. Supply chain managers can easily trace a product by using barcode scanners and attaching radio frequency identification devices to certain products. Big data analytics enables businesses to gather accurate product information so operators can stay on top of their distribution cycle. For instance, it will be easy for F&B managers to know when food spoilage is likely to occur.
Improved traceability ensures the tracking of goods from production to retail. Enhanced traceability enables businesses to better coordinate with supply chain stakeholders to streamline distribution.
Accurate forecasting to meet customer demand:
Big data sets are useful when businesses apply the gathered information about products to predict the requirements of customers. With accurate forecasting, businesses can improve profitability, predict customer demands, and reduce supply chain waste. Businesses are now using big data to predict customers’ preferences, while simultaneously accounting for external factors in the marketplace.
Enhanced relationship management:
According to the SCM world’s report (September 2014), 64% of supply chain executives think big data is an important and disruptive technology. Big data enable businesses to provide better customer service and improve relationships across the board. When supply chain managers have access to correct customer information at every stage, there is greater chance of fulfilling demands. Big data analytics also enables businesses to fix issues that arise in the distribution process.
Concluding thoughts
Big data analytics enables businesses to reduce costs, make faster decisions and develop new products to meet customer’s changing requirements. Big data analytics is providing supplier networks with greater data clarity, accuracy, and insights, leading to more contextual intelligence shared across supply chains.